Sun and Skin Cancer: Understanding the Link, Effective Prevention and Treatment Methods
Skin cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the skin cells. Skin cancer is a common type of cancer that occurs due to the exposure of skin cells to harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. It is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with over 5 million cases diagnosed each year.
There are three main types of skin cancer: Basal cell carcinoma, Squamous cell carcinoma, and Melanoma.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and various health agencies have extensively researched the link between sun exposure and skin cancer. This comprehensive health information aims, to provide an understanding of that link and outline multiple crucial measures to prevent skin cancer effectively.
The Link Between Sun and Skin Cancer
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation:
Prolonged and unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, whether from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds, is the primary cause of skin cancer. The three main types of UV radiation associated with skin cancer are UVA, UVB, and UVC. - DNA Damage and Mutations:
Ultraviolet radiation penetrates the skin and damages the DNA within skin cells. This disruption may lead to genetic mutations, triggering the uncontrolled growth of cells and potentially leading to skin cancer development.
Signs and Symptoms of Skin Cancer
- A new growth or sore that doesn’t heal.
- A change in the size, shape, or color of a mole or other spot on the skin.
- A spot or sore that is itchy, tender, or painful.
- A spot or sore that bleeds easily or doesn’t heal.
- A lump under the skin.
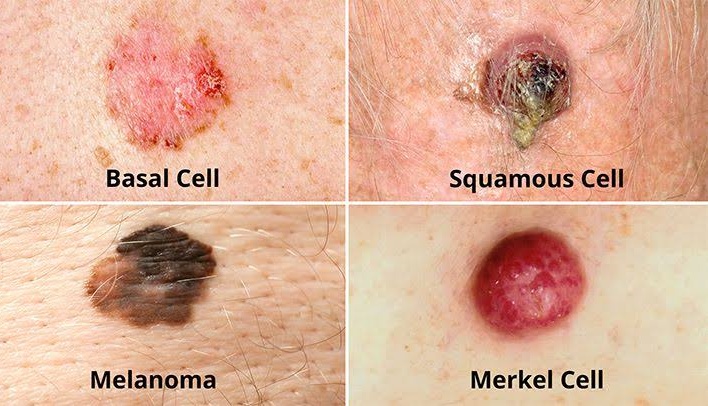
It’s important to regularly check your skin for any changes and to see a doctor if you notice any of these symptoms.
Various Ways and Methods to Prevent Skin Cancer
- Limit Sun Exposure: Seek shade: Stay in the shade during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm) when the sun’s UV rays are strongest. Use protection, wear wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and sunglasses with UV protection to reduce sun exposure to the skin.
- Apply Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen: Choose a sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or higher. Apply it generously on all exposed skin areas, including face, neck, hands, and feet. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating excessively.
- Cover Up: Wear protective clothing: Opt for lightweight, tightly woven clothing that covers the arms, legs, and other exposed areas. Use sun-protective accessories consider using umbrellas, sun-protective sleeves, or gloves to shield vulnerable skin areas from direct sun exposure.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer. It is best to avoid using tanning beds altogether.
- Check Your Skin Regularly: Perform self-examinations: Regularly examine your skin for any new moles, growths, or changes to existing moles. And consult a healthcare professional if you notice any suspicious skin changes, promptly consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
- Seek Shade: When outdoors, try to seek shade as much as possible, especially during the peak sun hours. This can help reduce your overall UV exposure and lower the risk of skin cancer.
- Be Sun-Smart on Cloudy Days: Even on cloudy or overcast days, UV rays can still penetrate through the clouds and cause damage to your skin. Therefore, it is important to apply sunscreen and follow sun protection measures regardless of the weather conditions.
- Educate Yourself about Ultraviolet Index: The UV Index is a scale that indicates the intensity of UV radiation levels in your area at a given time. Check the UV Index forecast regularly to determine the level of sun protection needed throughout the day.
- Protect Children: Children are more vulnerable to the sun’s harmful rays, so it is crucial to take extra precautions to safeguard their skin. Keep infants under six months of age out of direct sunlight and dress them in protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses. Apply sunscreen specifically formulated for children with a minimum SPF of 30.
- Promote Skin Cancer Awareness: Raise awareness among your family, friends, and community about the importance of sun protection and regular skin screenings. Encourage others to adopt sun-safe habits and educate them about the risks of skin cancer.
Read Also
Skin Cancer Treatment
The treatment for skin cancer depends on the type, size, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Treatment options for skin cancer may include:
- Surgery to remove the cancerous cells
- Radiation therapy to kill cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
- Immunotherapy to help the body’s immune system fight cancer
- Targeted therapy to attack specific molecules within cancer cells
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for a successful outcome in skin cancer cases. Treatment success rates are generally high for localized skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. However, melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, can be more dangerous and may require more intensive treatment.

In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can also help in preventing skin cancer. These include:
- Limiting exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds.
- Using sunscreen with a high SPF and reapplying it regularly.
- Wearing protective clothing, sunglasses, and hats when outdoors.
- Avoiding tanning beds and lamps.
- Regularly examining your skin for any changes and consulting a dermatologist for any suspicious spots or growths.
It’s essential to be proactive in protecting your skin from harmful UV rays and to monitor any changes in your skin to detect skin cancer early. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes in skin cancer cases.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to skin cancer. By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this potentially life-threatening condition. Alongside these preventive actions, it is also important to undergo regular skin cancer screenings by a healthcare professional, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or notice any changes in your skin.
Research by the WHO and other health agencies confirms the strong link between sun exposure and skin cancer. By adopting sun-safe habits and diligently following preventative measures, you can greatly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. Protect your skin from harmful Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, stay informed about the UV Index, and promote skin cancer awareness to ensure the long-term health and well-being of yourself and your loved ones.