Decoding Tinnitus: Understanding Hearing Loss and Problems

Hearing problems refer to any condition or impairment that affects a person’s ability to hear sounds clearly. These issues can range from mild to severe and may include difficulties with hearing certain frequencies, understanding speech, or experiencing ringing or buzzing sensations in the ears (tinnitus). Hearing problems can significantly impact one’s quality of life, affecting communication, social interactions, and even mental well-being.
Hearing loss is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. It occurs when there is damage to the structures in the ear that are responsible for hearing, such as the cochlea or auditory nerve. It’s essential to recognize the different types, causes, signs, and symptoms to effectively prevent and manage hearing issues.
Types and Causes of Hearing Problems
1. Conductive Hearing Loss: This type occurs when sound waves cannot pass through the outer or middle ear due to blockages, fluid buildup, or structural issues. Causes includes Ear infections, earwax buildup, otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth in the middle ear).
2. Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This type results from damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve. Causes includes Aging, exposure to loud noises, genetics, head trauma, certain medications, diseases (e.g., Meniere’s disease).
3. Mixed Hearing Loss: A combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Signs and Symptoms of Hearing Problems
1. Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments.
2. Needing to turn up the volume on electronic devices.
3. Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus).
4. Ear pain, itching, or discharge.
5. Feeling off-balance or dizzy (associated with inner ear issues).
6. Social withdrawal or frustration due to communication difficulties.
7. Speech and language development delays in children.
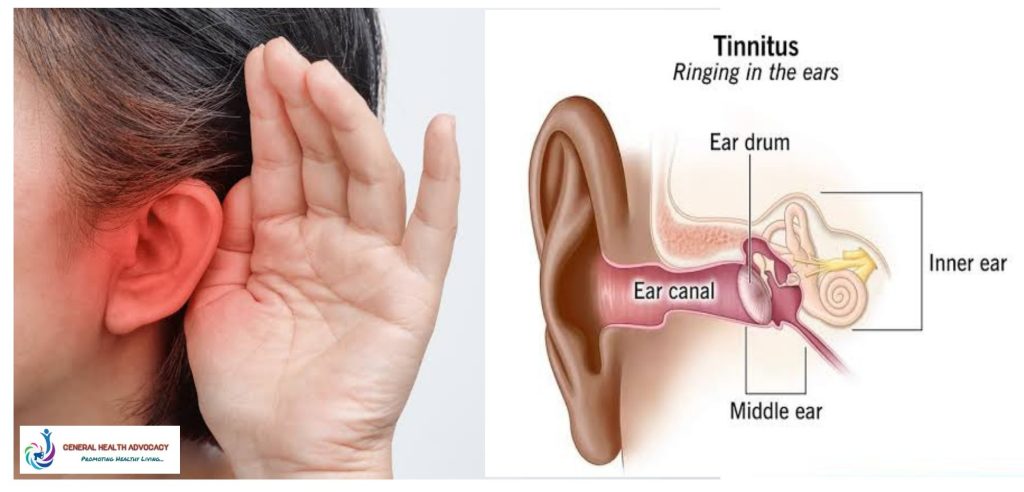
Understanding Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears when no external sound is present. It can be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system disorders. Tinnitus can be temporary or chronic and can vary in intensity from mild to severe. It can also be intermittent or continuous.
Causes of Tinnitus
There are many potential causes of tinnitus, including:
1. Hearing Loss: Damage to the hair cells in the inner ear, which can occur due to aging, exposure to loud noise, or other factors, can lead to tinnitus.
2. Ear Infections: Infections of the ear can cause inflammation and damage to the structures of the ear, leading to tinnitus.
3. Exposure to Loud Noise: Prolonged exposure to loud noise, such as listening to loud music or working in a noisy environment, can damage the hair cells in the inner ear and lead to tinnitus.
4. Earwax Buildup: Buildup of earwax can cause blockages in the ear canal, leading to tinnitus.
5. Certain Medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics, antidepressants, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause or worsen tinnitus as a side effect.
6. Medical Conditions: Tinnitus can also be associated with certain medical conditions, such as Meniere’s disease, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, and high blood pressure.

Signs and Symptoms of Tinnitus
The main symptom of tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. Other common symptoms may include:
- Buzzing, roaring, or hissing sounds
- Sensitivity to sound
- Difficulty sleeping
- Difficulty concentrating
- Anxiety or depression
Read Also
Prevention and Treatment of Tinnitus
While tinnitus can be challenging to treat, there are several strategies that may help manage symptoms:
1. Protect Your Hearing: Avoid exposure to loud noise and use ear protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, when necessary.
2. Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can worsen tinnitus symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques or counseling, may help.
3. Avoid Triggering Substances: Limit your consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, as these substances can worsen tinnitus symptoms for some people.
4. Seek Treatment for Underlying Conditions: If your tinnitus is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as hearing loss or an ear infection, seeking treatment for that condition may help alleviate tinnitus symptoms.
5. Sound Therapy: Sound therapy techniques, such as white noise machines or hearing aids that produce low-level background noise, may help mask the ringing or buzzing sounds of tinnitus.
6. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT techniques can help you learn to manage your reaction to tinnitus and reduce its impact on your daily life.
7. Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage tinnitus symptoms, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing tinnitus, as they can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Ways to Prevent and Control Hearing Problems
It’s essential to recognize the different signs and symptoms to effectively prevent and manage hearing issues. The prevention tips includes the following:
1. Protect Your Ears: Wear earplugs or earmuffs in loud environments such as concerts, construction sites, or when operating loud machinery.
2. Limit Exposure to Loud Noise: Keep electronic device volumes at a reasonable level and take breaks from noisy environments.
3. Maintain Ear Hygiene: Clean ears gently using a washcloth; avoid using cotton swabs, as they can push wax deeper into the ear canal.
4. Manage Health Conditions: Treat ear infections promptly, and manage chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, which can affect hearing.
5. Get Regular Check-ups: Routine hearing screenings can detect issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
6. Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of hearing loss, so quitting smoking can help preserve hearing health.
7. Stay Active: Regular exercise improves blood flow to the ears, supporting overall ear health.
8. Use Hearing Protection: When engaging in loud activities, wear protective gear to shield your ears from harmful noise levels.