Understanding Joint Pain: Comprehensive Guide to Manage Joint Pain
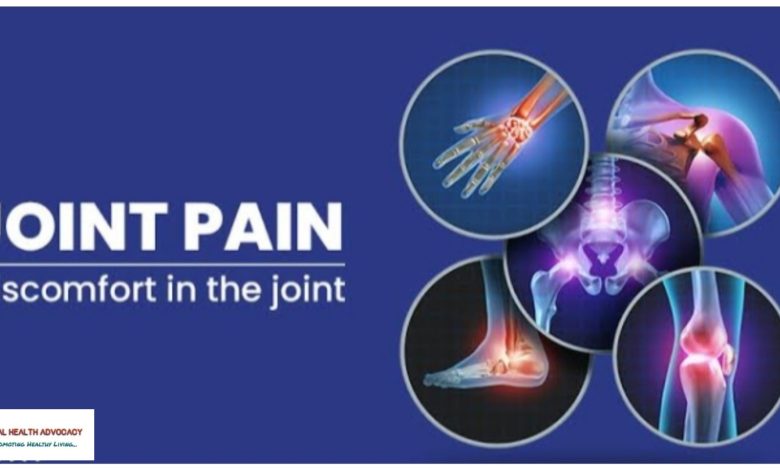
Joint pain refers to discomfort, aches, or soreness in any of the body’s joints. It can range from mild to severe and may be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting). Commonly affected joints include knees, hips, shoulders, and wrists.
Joint pain can significantly impact daily life, affecting mobility and overall well-being.
Causes of Joint Pain
1. Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of joint cartilage over time.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation.
3. Gout: Build-up of uric acid crystals in joints.
4. Injury: Sprains, strains, or fractures.
5. Overuse: Repetitive motion or excessive strain on joints.
6. Infection: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections in joints.
7. Other Conditions: Lupus, fibromyalgia, bursitis, etc.

Remedies for Joint Pain
1. Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate pain, adequate rest can help to relieve the pain.
2. Ice and Heat Therapy: Alternating cold packs and warm compresses.
3. Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen).
4. Topical Treatments: Creams or patches containing menthol or capsaicin, can help to relieve the pain.
5. Weight Management: Reducing excess weight to ease joint strain.
6. Exercise: Gentle stretching and low-impact activities like swimming or yoga, engage in moderate physical activities that is suitable for your body.
7. Dietary Changes: Avoiding foods that trigger inflammation (e.g., high purine foods for gout).
Read Also
Treatment for Joint Pain
1. Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles supporting joints.
2. Medications: Prescription drugs for inflammation or pain management.
3. Injections: Corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid injections into joints.
4. Surgery: For severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgeries.

When to See a Doctor
– Persistent Pain: Lasting more than a few days.
– Swelling or Redness: Around the joint.
– Difficulty Moving: Limited range of motion.
– Fever or Unexplained Symptoms: Alongside joint pain.
Prevention of Joint Pain
– Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on joints.
– Exercise Regularly: Strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
– Protect Joints: Use proper techniques during physical activities.
– Eat a Balanced Diet: Rich in nutrients that support joint health.
– Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of joint problems.
Joint pain can arise from various causes and affect people of all ages.
Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective management and treatment.
By incorporating lifestyle changes, appropriate therapies, and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can reduce pain, improve mobility, and maintain overall joint health.



Deirdra Juarranz